Is SAR really not affected by the atmosphere ?
Microwave remote sensing, typically Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) has been growing popular in the recent decades due to it’s ability to capture high resolution images of the earth regardless of the weather or time of day. Microwaves are able to penetrate atmospheric elements like clouds, fog and even some terrestrial objects like vegetation depending upon their wavelength.
As a result, there is a growing general consensus that SAR is completely immune to the effects of atmosphere. However, this is not 100% accurate. SAR is definitely less affected by the atmosphere compared to other sensors like optical sensors, but the effect is not entirely zero.
Attenuation of EM waves by atmosphere
All Electromagnetic (EM) waves such as radar waves, light waves are attenuated by atmospheric elements such as clouds, rains and fogs. The extent to which any wave is attenuated by the atmosphere depends on the frequency / wavelength of this wave. This can be better understood using the graph shown below:
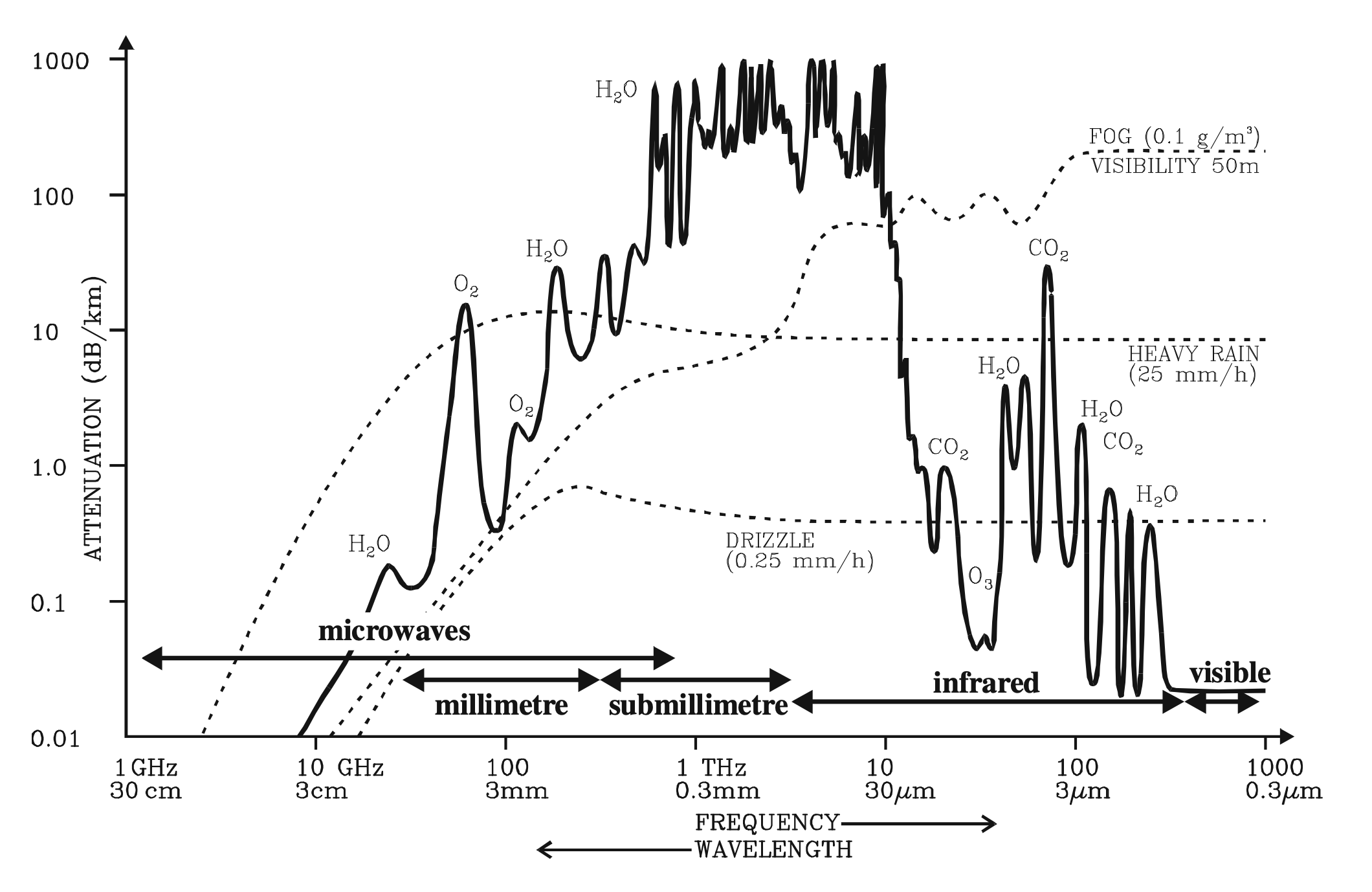
The above graph shows that microwaves cover a wide range of frequencies / wavelengths. Microwaves with frequencies above 10GHz are typically more attenuated by atmospheric elements compared to lower frequencies. Above 10 GHz, the attenuation effects show an exponential increase.
Modern X-band SAR satellites usually operate in the frequency range of around 10 GHz. We can see from the graph that even at 10 GHz frequency, the attenuation effects start to be visible. On the other hand, some other band of SAR satellites such as C-band (4 GHz - 8 GHz), L-band (1 GHz - 2 GHz), etc have almost zero attenuation from the atmosphere.
With this in context, we can conclude that SAR satellite based remote sensing is not completely immune to atmospheric effects. SAR satellites operating in some frquencies are affected more than the ones operating in some other frequencies. The sensor wavelength for any use-case should be ultimately selected based on the desired results. There is always a trade-off between various parameters such as atmospheric effects, pentration depth, image costs, resolution etc.
References
- Woodhouse, I.H. (2006). Introduction to Microwave Remote Sensing (1st ed.). CRC Press.
- Peckham, G. E. (1991). Instrumentation and measurement in atmospheric remote sensing. Reports on Progress in Physics, 54(4), 531.